Discover how to check app permissions to protect your privacy and control what information your apps can access.
You can easily see which permissions an app has by going to your device’s settings, selecting the app, and reviewing the list of allowed permissions.
This gives you a clear view of what each app can do, such as accessing your camera, contacts, or files.
Understanding app permissions helps you decide what access is necessary and what might be too much.
Whether you use a smartphone or a computer, managing these settings ensures you keep control over your personal data and avoid unwanted access by apps.
By knowing how to check and adjust app permissions, you can prevent apps from using features or information you don’t want to share.
This simple action can improve your security and give you peace of mind with the apps you use every day.
Understanding App Permissions
App permissions control what parts of your device apps can access. They affect your privacy and security by deciding which data or features an app can use. Knowing how permissions work helps you protect your personal information and avoid unwanted access.
What Are App Permissions
App permissions are requests made by apps to access features or data on your device. For example, an app may ask for permission to use your camera, contacts, or location. These permissions must be granted for the app to use those functions.
Permissions are often requested when you open the app for the first time or when the app needs a specific feature. You can either allow or deny these requests. If you deny permission, some app features may not work properly.
Understanding what each permission means is important. It helps you decide which permissions are necessary. Permissions give apps access to sensitive parts of your device, so reviewing them carefully can protect your privacy.
Why App Permissions Matter
App permissions affect your privacy because they determine what data an app can collect and use. For example, if an app has access to your microphone or camera, it could potentially record audio or video without your knowledge if misused.
Managing permissions also improves device security. By limiting unnecessary access, you reduce the risk of data leaks or malicious activity. Apps with fewer permissions have fewer chances to harm your data.
You should check app permissions regularly, especially after updates. Sometimes apps add new permissions in updates that you may not want to grant. Being aware of your permission settings helps maintain control over your personal information.
Common Types of App Permissions
Here are some common app permissions and what they allow:
- Camera: Lets the app take photos and videos.
- Microphone: Allows recording sounds or voice.
- Contacts: Grants access to your contact list.
- Location: Shares your device’s location for maps or tracking.
- Storage: Lets the app read or save files on your device.
- Phone: Allows access to call and SMS features.
Each permission affects your privacy differently. For example, camera and microphone permissions are sensitive because they can capture media. Always check if the app’s purpose matches the permissions it requests before granting access.
How to Check App Permissions on Windows 11
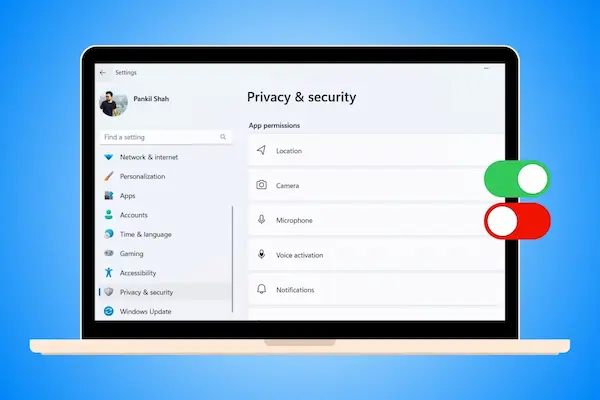
You can control which apps have access to your data and hardware in Windows 11. This helps protect your privacy and lets you decide what each app can do. The process involves opening privacy settings, checking what permissions an app has, and changing them if needed.
Accessing Privacy & Security Settings
Start by opening the Windows 11 Settings app. You can press Windows key + I or click the Start menu and select Settings.
Next, click on Privacy & Security in the left-hand menu. This section shows all privacy-related options.
Scroll down to see categories like Camera, Microphone, Location, and Contacts. Each category controls permissions for apps using those features.
This area acts as the main hub where you can review and manage which apps have access to sensitive parts of your device.
Viewing and Modifying App Permissions
In the Privacy & Security settings, select a category such as Camera or Location.
You will see a list of apps that have requested permission to use this feature. The list shows if permission is On or Off for each app.
Click the toggle switch next to an app to enable or disable its access.
If you want to check permissions for multiple types like your microphone or contacts, repeat this process for each category.
Modifying permissions here lets you protect your personal data by limiting app access to only what is necessary.
Allowing or Denying Permissions for Specific Apps
If you want to allow or deny permissions for a specific app, find it under the relevant category in Privacy & Security.
For example, to control camera access, go to Camera permissions and look for the app’s name.
Switch its permission On if you want it to use the camera. Switch it Off if you want to deny access.
You can also remove permissions for apps that no longer need them, helping maintain better control over what apps can do on your system.
Regularly reviewing these settings ensures you only grant necessary permissions to trusted applications.
App Permissions on Windows 10
Windows 10 lets you control which apps can access your device features and data. You can find and change these permissions easily through your system settings. Pay close attention to important features like location service to protect your privacy.
Navigating to App Permissions
To check app permissions, start by opening Settings from the Start menu. Then click on Privacy. On the left side, you will see a list of permission categories like Camera, Microphone, and Location.
Select the category you want to review. You will see which apps are allowed to use that feature. You can toggle permission on or off for individual apps here.
This panel helps you view permissions all in one place instead of searching through each app separately. It gives you clear control over what data or device features apps can access.
Editing Permissions for Installed Apps
If you want to change permissions for a specific app, open Settings and go to Apps > Installed apps. Find the app in the list.
Click on the app, then choose Advanced options. Look for the App permissions section. Here, you will see all the permissions the app can request, such as camera or microphone access.
You can turn off any permission that you think isn’t necessary for the app to work. This helps limit apps from accessing more than they need.
Keep in mind some apps might not work properly if you disable essential permissions. Adjust permissions carefully based on your needs.
Managing Location Service Settings
Location service permissions are especially important because they let apps know where you are. To manage these, open Settings > Privacy > Location.
First, ensure the switch for Allow access to location on this device is turned on if you want apps to use your location. Underneath, you will see a list of apps and whether they can use location data.
You can enable or disable location permission for each app independently. You will also find a central toggle for turning off location service completely, if you prefer maximum privacy.
Turning off location can stop some apps from working correctly, especially maps and weather apps. You should review which apps need location service and decide accordingly.
Checking App Permissions on Mobile Devices
You can see which apps have access to your camera, microphone, location, and more. Managing these permissions helps protect your privacy and control what each app can do on your device. It’s important to check permissions regularly and remove access when it is not needed.
How to Review Permissions on Android
On Android, open your Settings app and go to Apps or Apps & notifications. From there, select App permissions or Permission manager. You’ll see a list of permission types like camera, microphone, or location.
Tap a permission to view which apps currently have access. You can also see when an app last used a permission on some Android versions. This helps you decide if any app is using permissions unnecessarily.
You can change permissions by toggling apps on or off for each type. Android 12 and newer versions offer a Privacy dashboard to track usage history, which is useful to monitor apps’ permission use over time.
How to Manage Permissions on iOS
On iOS, open Settings and scroll down to find the list of your apps. Tap an app to see its permission options. You can allow or deny access to things like location, camera, microphone, photos, and notifications.
Alternatively, go to Privacy & Security in settings to see permissions by type and which apps have access. For example, under Location Services, you can adjust access for all apps needing location data.
iOS lets you select options like “While Using the App,” “Always,” or “Never” for location permissions. Tailoring these settings reduces unnecessary data sharing and increases your control over what apps can do.
Revoking Permissions for Unused Apps
If you no longer use an app, revoke its permissions to protect your data. You can either remove specific permissions or uninstall the app altogether.
On Android, go to Apps in settings, select the app, and tap Permissions. Turn off all permissions the app does not need anymore.
On iOS, either go to the app’s settings and toggle permissions off or delete the app.
Removing permissions for unused apps lowers the risk of data being accessed without your knowledge and helps keep your device secure. Regularly review permissions to stay in control.
Best Practices for Managing App Permissions
Managing app permissions well means controlling what information apps can access and protecting your privacy. You should check permissions often, understand why apps ask for certain access, and use strategies to limit data exposure only to what is necessary.
Review Permissions Regularly
You should review app permissions regularly to keep control over your data. Check which apps have access to sensitive information like your location, microphone, camera, and contacts. Remove or restrict permissions for apps you no longer use or apps that request access for no clear reason.
Many devices let you see all app permissions in one place. On iOS and Android, you can open settings and view permissions by app or permission type. Focus on apps that have broad access to your data and remove access if it is not needed for the app’s core function.
Regular reviews help reduce the risk of your data being shared or sold without your knowledge. If an app asks for permission you find uncomfortable, it’s often safer to deny it or uninstall the app entirely.
Tips for Enhancing Privacy & Security
Use these tips to improve your privacy and security when managing app permissions:
- Only install apps from trusted sources like the Apple App Store or Google Play Store.
- Turn off permissions you don’t need. For example, disable location access if the app doesn’t use it for key features.
- Limit location access to “Only While Using.” This restricts the app from tracking your location when it’s not open.
- Remove unused apps. Even inactive apps with permissions can expose your data.
- Check each app’s privacy policy to understand how your information is handled and shared.
Using these methods lowers chances that your personal data falls into the wrong hands or is used without your permission.
Understanding Permission Requests
When an app asks for permission, you need to carefully evaluate if the request makes sense. Many apps request access to perform specific functions. However, some may ask for more access than needed.
Ask yourself:
- Does this app need the permission to work?
- Does the permission match the app’s main features?
- Could granting access pose a risk to my privacy?
If you’re unsure, deny the request or look up the app’s reviews and privacy policy for more information.
Be cautious with permissions involving location, camera, microphone, contacts, and text messages, as these can reveal a lot about you. You can always allow access temporarily and revoke it later if you find the app misuses your data.